Part 2 of the 2 part article on how music affects your brain.
7. Your heartbeat changes to mimics the music you listen to.
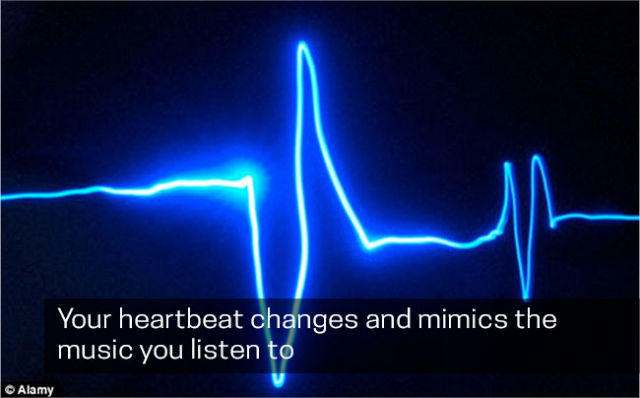
Music is found to modulate heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration. The cardiovascular system mirrored deflating decrescendos, and swelling crescendos in a study of 24 volunteers. Distinguishing changes in sound patterns were even found to be equipped in those as small as a developing fetus.
8. Listening to happy vs. sad music can affect the way you perceive the world around you.
The brain always compares the information that comes through the eyes with what it expects about the world, based on what you know. The final results in our mind is what we perceive as our reality. Therefore, happy songs that lift your spirits make you see the world around you differently then that of a sad person.(source)
9. An “earworm” is a song that you can’t seem to get out of your head.

An earworm is a cognitive itch in your brain. This “brain itch” is a need for the brain to fill in the gaps in a song’s rhythm. The auditory cortex is a part of your brain that will automatically fill in a rhythm of a song. In other words, your brain kept “singing” long after the song had ended.(source)
10. Music triggers activity in the same part of the brain that releases Dopamine, the “pleasure chemical”.
The nucleus accumbens is a part of your brain that releases Dopamine during eating, and sex. The most interesting part, is that the nucleus accumbens is just a small part of the brain that gets effected by music. It also effects the amygdala, which is the part of the brain used to process emotion. for music.(source)
11. Music is often prescribed to patients with Parkinson’s Disease and stroke victims.

Music therapy has been around for decades. Music triggers networks of neurons into organized movement. The part of the brain the processes movement also overlaps speech networks. These two key elements help patients overcome the obstacles that most effect them such as basic motor skills, and speech difficulties.(source)
12. According to a study, Learning a musical instrument can improve fine motor and reasoning skills.

In a study of children, it revealed that those with three or more years of musical training preformed better in fine motor skills and auditory discrimination abilities then those who had none. They even tested better for vocabulary and reasoning skills, even though those are quite separate from music training.(source)
